The Next Phase of Payment Infrastructure
The evolution of payment systems has introduced innovative solutions to address persistent challenges in modern commerce. Reverse ATM and cash to card technology represents a sophisticated approach to bridging the gap between traditional cash transactions and digital payment ecosystems.
This guide explores the architecture, capabilities, and strategic applications of reverse ATM systems—tools that enable businesses to operate cashless environments while maintaining accessibility for customers who rely on cash.
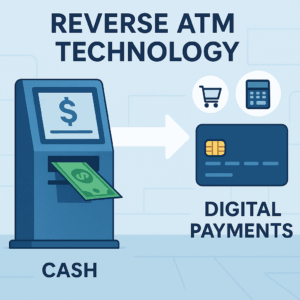 Defining Reverse ATM Technology
Defining Reverse ATM Technology
Reverse ATMs function as the inverse of traditional ATMs. Instead of dispensing cash from digital accounts, they accept cash deposits and issue digital payment credentials.
The term "reverse ATM" encompasses several implementations:
- Cash-to-card kiosks
- Cash exchange stations
- Automated currency conversion systems
All share a common purpose: converting physical currency into immediately usable digital instruments within controlled environments.
Modern systems extend beyond basic conversion. They frequently include:
- Account management features
- Balance inquiries and transaction histories
- Reload and reissue capabilities
These features transform reverse ATMs from single-purpose converters into full-featured payment terminals, combining the efficiency of cashless operations with inclusivity for cash-preferring users.
Technical Architecture and System Components
Reverse ATMs and cash to card solutions integrate multiple subsystems that coordinate to deliver reliable, secure functionality.
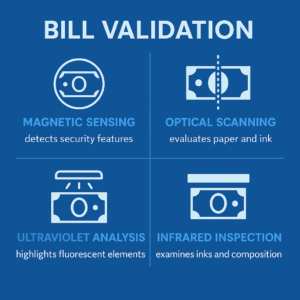
Bill Validation
The first stage of any transaction is authenticating the deposited cash. Modern bill acceptors use multiple technologies simultaneously:
- Magnetic sensing
- Optical scanning
- Ultraviolet and infrared analysis
Together, these achieve 99.9%+ accuracy while maintaining high processing speed, rejecting counterfeit or damaged bills before storage.
Secure Cash Storage
Validated currency is transferred into reinforced storage compartments featuring:
- Hardened materials and locking systems
- Tamper-evident seals
- Sensors that track capacity and trigger collection alerts
This layered approach ensures physical protection and precise reconciliation of funds.
Card Dispensing
The transaction concludes when a prepaid card is issued, encoded with the deposited value. Dispensing mechanisms are engineered for reliability, with sensors verifying encoding success before release. This minimizes service interruptions, even under high throughput.
Software Architecture and Transaction Processing
While the hardware provides the visible interface, software orchestrates the transaction flow.
Core functions include:
- Account creation and balance allocation
- Fraud detection and real-time authorization
- Integration with POS infrastructure
Real-time communication protocols ensure immediate activation and balance availability. Systems maintain data consistency across terminals—even during temporary outages—through automatic offline reconciliation. Modern platforms support multiple integration methods, from RESTful APIs to legacy protocols, allowing operators to implement reverse ATMs without replacing existing infrastructure.
 Advanced Bill Validation Technology
Advanced Bill Validation Technology
As counterfeiting grows more sophisticated, multi-spectral imaging has become the industry standard. By capturing bill characteristics across visible, ultraviolet, and infrared wavelengths, systems create unique digital "signatures" for each note. Machine learning algorithms enhance detection by identifying subtle anomalies and improving with each transaction. Systems also assess the physical condition of bills, rejecting those too damaged for storage or bank processing. International deployments may add multi-currency functionality, managing validation and conversion with separate storage compartments and exchange-rate logic.
Security Architecture and Threat Mitigation
Reverse ATMs must defend against both physical and digital threats.
Physical Security
- Hardened enclosures and anchoring systems
- Tamper sensors and intrusion alerts
Cybersecurity
- End-to-end encryption (in transit and at rest)
- Compliance with NIST standards for encryption and key management
- Secure network communications via VPN tunneling and intrusion detection
- Automated containment to isolate compromised nodes
This defense-in-depth model ensures operational integrity and customer trust.
Transaction Speed and Throughput
Customer satisfaction depends on speed and reliability. Advanced systems complete transactions—from bill insertion to card issuance—in under 30 seconds.
Key performance characteristics:
- High-speed validators processing multiple bills per second
- Parallel processing during validation and storage
- Optimized dispensing mechanisms with jam detection
- In-memory databases and distributed architectures to reduce latency
The result: thousands of concurrent transactions with consistent performance, even during peak usage.
User Interface Design and Accessibility
Interface design determines how easily customers adopt new systems. Effective reverse ATMs emphasize clarity, accessibility, and inclusivity through:
- Large, high-contrast touchscreen layouts
- Simple, step-by-step guidance
- Multilingual and visual prompts
- ADA-compliant accessibility features (audio guidance, tactile feedback, screen-reader compatibility)
By incorporating these principles, operators expand usability and comply with accessibility standards while improving the customer experience.
Technical FAQ
What security standards must reverse ATMs meet?
PCI DSS: Required for systems processing or transmitting cardholder data.
NIST Guidelines: Provide robust encryption and key-management frameworks.
AML/KYC: Transaction monitoring and suspicious-activity flagging to ensure compliance with anti-money-laundering laws.
How do multi-spectral bill validators achieve 99.9% accuracy?
Through sensor fusion and algorithmic cross-validation across multiple light spectrums:
- Visible light checks print quality and watermarks.
- UV light reveals fluorescent inks and strips.
- IR light analyzes magnetic and ink properties.
Hundreds of data points are verified against secure, continually updated databases.
What's the technical difference between magnetic stripe and EMV chip encoding?
| Feature |
Magnetic Stripe |
EMV Chip |
| Data Storage |
Static, linear tracks |
Encrypted, dynamic chip memory |
| Security |
Static—susceptible to cloning |
Dynamic—unique cryptogram per transaction |
| Fraud Risk |
Higher |
Significantly reduced |
Performance Analytics and Business Intelligence
Each transaction generates valuable operational and behavioral data.
- Transaction volumes → identify peak periods and staffing needs
- Customer behavior → reveal deposit size, usage frequency, and reload patterns
- System reliability metrics → track uptime, success rates, and processing times
These data streams form the foundation for continuous optimization, guiding decision-making, cost control, and customer-experience improvements.
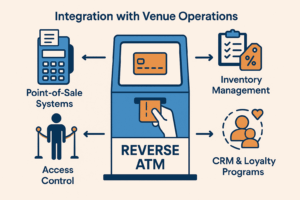 Integration with Venue Operations
Integration with Venue Operations
Cash to card kiosks deliver maximum value when integrated into venue ecosystems.
Basic integrations:
- POS and payment terminal compatibility
Advanced integrations:
- CRM and loyalty systems for personalized offers
- Access control systems (e.g., gates, lockers, or amenities)
- Inventory management for event or retail venues
This connectivity transforms reverse ATMs into strategic customer engagement tools, not just transactional utilities.
Maintenance and Reliability
Uptime is critical. Maintenance programs emphasize proactive reliability engineering:
- Preventive maintenance based on component lifecycles
- Remote diagnostics and predictive analytics
- Tiered firmware updates with rollback options
- Spare-parts management to balance availability and cost
Together, these practices sustain consistent service quality across large deployments.
Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management
Reverse ATMs intersect with multiple financial and consumer protection frameworks:
- Money transmission laws (jurisdiction dependent)
- AML/KYC requirements for transaction monitoring
- Consumer protection for fee transparency and dispute resolution
Designing systems with compliance in mind not only avoids legal risk but also builds customer confidence in system integrity.
Emerging Technologies and Future Developments
The reverse ATM and cash to card sector continues to evolve through innovation and convergence:
- Blockchain integration for immutable transaction records
- Biometric authentication to replace physical cards
- AI-driven fraud detection and predictive maintenance
- Mobile wallet integration enabling digital card issuance via app
These advances align reverse ATMs with omnichannel payment strategies, unifying physical and digital experiences.
Industry Applications
Reverse ATMs are already proving value across industries:
- Entertainment Venues & Stadiums: Accelerate concession sales during peak times
- Transit Systems: Reduce fare-collection costs while serving unbanked riders
- Universities: Integrate with student ID systems for dining and retail
- Corporate Campuses: Enable cashless cafeterias via employee badges
These case studies illustrate the technology's versatility and measurable operational benefits.
Strategic Implementation
Successful deployment requires strategic planning and change management:
- Define requirements (transaction volume, integrations, security).
- Pilot programs to validate assumptions and optimize workflows.
- Staff training for support and customer guidance.
- Awareness campaigns to encourage adoption and address concerns.
- Feedback loops for continuous improvement post-launch.
This structured approach maximizes both ROI and customer satisfaction.
Technical Specifications and Standards Appendix
Compliance Framework
Payment Card Industry Standards
- PCI DSS v4.0 compliance for cardholder data protection
- PA-DSS validation for payment applications
- P2PE certification for point-to-point encryption
Federal Standards and Guidelines
- NIST SP 800-57 Part 1 Rev. 5: Key Management Framework
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework v1.1: Core security functions
- FIPS 140-2 Level 3: Cryptographic module standards
- AES-256 encryption for data at rest and in transit
Financial Regulatory Compliance
- BSA/AML compliance for transaction monitoring
- FinCEN guidance on money transmission (varies by jurisdiction)
- Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) regulations
- State money transmitter licensing requirements
Performance Benchmarks
Transaction Processing
- Bill validation: <3 seconds per note
- Card encoding and dispensing: <10 seconds
- Complete transaction cycle: <30 seconds
- System throughput: 120+ transactions/hour (sustained)
- Uptime requirement: 99.5% availability
Security Metrics
- Counterfeit detection rate: >99.9%
- False positive rate: <0.1%
- Encryption strength: AES-256 with RSA-4096 key exchange
- Tamper detection response: <5 seconds
Hardware Specifications
- Bill acceptor capacity: 500-2,000 notes (model dependent)
- Card dispenser capacity: 100-500 cards
- Environmental operating range: 32°F to 104°F (0°C to 40°C)
- Network connectivity: Ethernet, Wi-Fi 802.11ac, cellular backup
Regulatory Framework Matrix
| Jurisdiction |
Money Transmission License |
Transaction Limits |
Reporting Requirements |
| Federal (US) |
MSB registration if >$1,000/day |
Varies by state |
CTR for >$10,000 |
| California |
Required for stored value |
No daily limits |
Monthly reconciliation |
| New York |
BitLicense for virtual currency |
$5,000/day individual |
Real-time monitoring |
| European Union |
EMD2 compliance |
€250 anonymous limit |
AMLD5 reporting |
Integration Standards
API Specifications
- RESTful API with JSON formatting
- OAuth 2.0 authentication
- Webhook support for real-time notifications
- Rate limiting: 1,000 requests/minute
POS Integration Protocols
- ISO 8583 messaging standard
- EMV L2 certification
- Contactless payment support (NFC, RFID)
- Legacy magnetic stripe compatibility
Data Exchange Formats
- Transaction logs: ISO 20022 XML standard
- Settlement files: NACHA ACH formatting
- Audit trails: SIEM-compatible CEF format
Conclusion
Reverse ATM technology has become essential infrastructure for organizations seeking to combine the efficiency of cashless operations with the inclusivity of cash-accepting services. By uniting advanced hardware, intelligent software, and robust security architecture, these systems deliver measurable operational and customer-experience value. As payment ecosystems evolve, these cash to card kiosks will remain cornerstone tools—bridging the physical and digital worlds of modern commerce.

 Defining Reverse ATM Technology
Defining Reverse ATM Technology Advanced Bill Validation Technology
Advanced Bill Validation Technology Integration with Venue Operations
Integration with Venue Operations