 The transition from cash-based to digital payment environments presents both opportunities and challenges for venue operators across diverse industries. Custom prepaid card programs offer sophisticated solutions that maintain operational efficiency while serving customers who prefer or require alternatives to traditional payment methods.
The transition from cash-based to digital payment environments presents both opportunities and challenges for venue operators across diverse industries. Custom prepaid card programs offer sophisticated solutions that maintain operational efficiency while serving customers who prefer or require alternatives to traditional payment methods.
This guide examines the business case, implementation framework, and optimization strategies for prepaid card programs that deliver measurable value to both operators and customers.
The Strategic Business Case for Prepaid Programs
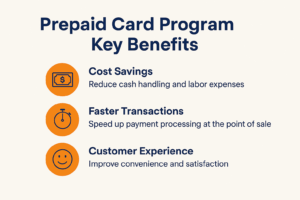
Prepaid card programs provide value that extends well beyond simple payment processing. They support operational efficiency, improve customer experience, and generate strategic business intelligence that can reshape decision-making. The most immediate benefit comes from operational cost reduction. Traditional cash handling requires staff for counting, reconciliation, deposits, and change management, all of which introduce human error and security risks. Prepaid systems eliminate much of this overhead while also reducing theft and shrinkage.
They also improve transaction speed. Cash exchanges slow lines during peak periods, while prepaid transactions process in seconds. Faster throughput increases venue capacity without requiring additional staff. For operators, this translates directly into revenue growth and improved customer satisfaction due to shorter wait times.
Finally, prepaid programs unlock data analytics. Unlike cash, every prepaid transaction is traceable, generating insights into customer preferences, spending behavior, and visit frequency. This intelligence supports better inventory planning, pricing strategies, and targeted marketing campaigns. Operators gain efficiency, revenue potential, and actionable customer insights while delivering a smoother, more modern payment experience.
Program Architecture and Design Considerations
Design decisions made at the outset of a prepaid program determine its long-term success. These include architecture type, account structure, card technology, and system integration.
One of the first choices is between closed-loop and open-loop architectures. Closed-loop programs limit usage to specific venues or networks, giving operators full control and simplified compliance. Open-loop programs, typically tied to major card networks, allow wider acceptance but bring more regulatory obligations and complexity. The choice depends on whether the goal is maximum control or maximum flexibility.
Account structures vary as well. Single-use disposable cards require minimal infrastructure but limit customer engagement. Reloadable cards encourage repeat use, building ongoing relationships and reducing per-transaction costs. Hybrid approaches offer flexibility to serve both one-time visitors and loyal customers.
Card technology influences functionality and security. Magnetic stripe cards are inexpensive and broadly compatible but less secure. Chip-based cards add fraud protection and enable contactless features. Dual-interface cards combine both for maximum flexibility and future-proofing.
Finally, integration architecture determines whether the system runs standalone or connects with existing platforms such as POS, inventory management, or CRM systems. Standalone models are simpler to launch, while integrated systems unlock greater efficiency and richer data insights. Careful architectural choices align program capabilities with venue strategy, balancing ease of deployment with long-term growth potential.
Card Design and Branding Strategy
Physical card design is more than a technical detail — it is a brand extension that customers carry in their wallets. Colors, typography, and graphics should reinforce brand identity while remaining legible and durable through everyday use. Functional elements like magnetic stripes, EMV chips, and printed numbers must comply with payment standards. Security elements such as holograms, microprinting, or color-shifting inks not only deter fraud but also communicate trustworthiness.
Many venues also create collectible or limited-edition cards tied to events, holidays, or special promotions. These designs increase engagement by appealing to customer pride and loyalty, encouraging repeat visits and ongoing retention of the card as a keepsake. Well-designed prepaid cards double as portable marketing assets that strengthen brand presence far beyond the venue.
Technology Infrastructure and System Integration
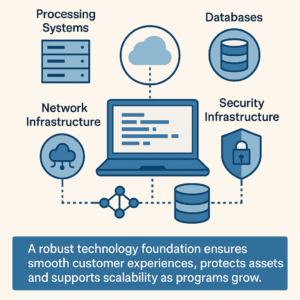 Reliable infrastructure underpins every prepaid program. At the core, processing systems handle account creation, balance tracking, and transaction authorization. High availability is essential, requiring redundant components and peak-capacity planning to avoid service interruptions. Databases store account and transaction information and must be protected through strong backup protocols, geographic redundancy, and encryption. Optimized query performance supports fast customer interactions. Network infrastructure links terminals, kiosks, and administrative systems. Redundant connections and offline-capable designs prevent outages from disrupting service, while synchronization ensures balances remain accurate across systems.
Reliable infrastructure underpins every prepaid program. At the core, processing systems handle account creation, balance tracking, and transaction authorization. High availability is essential, requiring redundant components and peak-capacity planning to avoid service interruptions. Databases store account and transaction information and must be protected through strong backup protocols, geographic redundancy, and encryption. Optimized query performance supports fast customer interactions. Network infrastructure links terminals, kiosks, and administrative systems. Redundant connections and offline-capable designs prevent outages from disrupting service, while synchronization ensures balances remain accurate across systems.
Finally, security infrastructure is paramount. Encryption, access controls, intrusion detection, and layered monitoring safeguard both financial and personal data. A robust technology foundation ensures smooth customer experiences, protects assets, and supports scalability as programs grow.
Customer Acquisition and Program Launch
A strong launch strategy is critical for adoption. Preparation begins with staff training so employees can explain benefits, help with enrollment, and troubleshoot issues. Sports arenas and stadiums have successfully deployed these systems to streamline payment processes and enhance customer experience. Marketing should use multiple channels — digital, in-venue signage, and direct staff engagement — to raise awareness. Promotions such as bonus value on first loads or discounts for early adopters reduce barriers and build momentum.
Many operators employ a soft launch, releasing the program to a limited audience before full rollout. This controlled approach allows time to identify system issues, refine communications, and incorporate feedback. Once stable, a high-visibility launch event can generate excitement and customer enthusiasm. A well-executed launch establishes confidence, drives adoption, and positions the program for long-term success.
Promotional Strategies and Customer Incentives
Prepaid card programs thrive on continuous engagement. Promotions can target acquisition, usage, reloads, or partnerships. Acquisition offers — such as bonus credits or limited-time discounts — reduce entry barriers. Usage promotions encourage higher spending or frequency, while reload incentives keep accounts active and increase transaction values. Partnership promotions with complementary businesses can expand reach and create co-branded experiences, deepening value for customers. Strategic incentives sustain engagement, increase card loads, and maximize lifetime customer value.
Operational Management and Customer Service
Operational excellence is the backbone of prepaid program success. Daily processes include secure balance management, dispute resolution, and card inventory tracking These versatile systems efficiently handle multiple operational processes across different venue types. Customer service must cover common needs: balance inquiries, lost card replacements, and transaction disputes. Offering multiple support channels — from in-person to self-service via apps — ensures accessibility. Clear dispute resolution policies protect both customers and operators. Strong operations and service build trust, reduce churn, and keep programs running smoothly.
Financial Management and Accounting
Prepaid programs carry unique accounting requirements. Funds received from customers must be tracked as prepaid liabilities until redeemed. Regular reconciliation ensures system balances match actual funds. Unused balances, known as breakage, can be recognized as revenue depending on regulations, but conservative policies help maintain compliance and trust.
Programs may also generate revenue from fees such as issuance, reloads, or inactivity — all of which must be transparent and legally compliant. Careful cash flow management ensures float balances remain sufficient for redemption while enabling operators to maximize investment opportunities. Proper financial management ensures regulatory compliance and protects both customer confidence and operator stability.
 Data Analytics and Business Intelligence
Data Analytics and Business Intelligence
Prepaid transactions provide a wealth of data that cash cannot. Segmenting customers by spending habits, visit frequency, or reload behavior allows for tailored engagement strategies. Predictive analytics can forecast churn, enabling preemptive retention efforts, while lifetime value modeling helps justify acquisition investments. Purchase patterns guide inventory management and pricing decisions. A/B testing can be applied to promotions, communications, and program features, providing evidence-driven improvements. Analytics turn payment data into strategic intelligence that supports smarter business decisions and more personalized customer engagement.
Regulatory Compliance and Legal Considerations
Prepaid programs operate within a complex regulatory environment. Consumer protection rules require clear disclosure of fees, terms, and expiration policies. State-by-state escheatment laws govern unclaimed balances, requiring transfer to state authorities after dormancy periods. Open-loop programs must also comply with major payment network rules, including PCI DSS for security. Meanwhile, data privacy laws such as GDPR add requirements for transparency, customer consent, and rights management. Proactive compliance avoids legal penalties, protects brand reputation, and builds customer trust.
Mobile Integration and Digital Innovation
Mobile technology expands prepaid program capabilities. Dedicated apps allow customers to check balances, reload accounts, and view history anytime. Push notifications deliver promotions or low-balance alerts. Integration with digital wallets like Apple Pay or Google Pay extends usability to contactless payments, while QR codes offer quick, card-free transactions. Geolocation services enable proximity-based promotions or fraud detection. Digital integration improves convenience, engagement, and operational flexibility, making prepaid programs more attractive to modern consumers.
Program Evolution and Continuous Improvement
No prepaid program is static. Regular customer feedback, competitor analysis, and technology upgrades ensure ongoing relevance. Infrastructure refresh cycles and benchmarking against industry best practices help maintain performance. Continuous improvement protects competitiveness and ensures programs remain aligned with customer expectations.
Strategic Partnership Opportunities
Partnerships extend program reach and value. Co-branded cards deepen brand associations, while loyalty program integrations tie prepaid usage to rewards. Retail distribution partnerships expand accessibility, and technology partnerships reduce development costs while enhancing features. Strategic alliances enhance program appeal, expand reach, and create competitive differentiation.
Conclusion
 Custom prepaid card programs deliver strategic value that far exceeds payment processing. They reduce costs, accelerate transactions, enhance customer experience, and provide valuable business intelligence. Organizations considering implementation often have questions about deployment, which should be addressed early in the planning process. By asking the right questions from the start of the project, designing thoughtful architecture, building robust infrastructure, engaging customers through promotions, and maintaining operational excellence, operators can create programs that deliver both immediate and long-term benefits.
Custom prepaid card programs deliver strategic value that far exceeds payment processing. They reduce costs, accelerate transactions, enhance customer experience, and provide valuable business intelligence. Organizations considering implementation often have questions about deployment, which should be addressed early in the planning process. By asking the right questions from the start of the project, designing thoughtful architecture, building robust infrastructure, engaging customers through promotions, and maintaining operational excellence, operators can create programs that deliver both immediate and long-term benefits.
As payment ecosystems evolve, prepaid programs offer flexible platforms that adapt to new technologies and customer expectations. They represent not just a payment method but a competitive advantage for venues seeking to thrive in a digital-first environment.
Custom Prepaid Card Programs FAQ
- What's the typical implementation timeline for a custom prepaid program?
Implementation typically takes 3-6 months depending on complexity, including system integration, compliance review, card design, staff training, and pilot testing phases.
- How do closed-loop and open-loop programs differ in regulatory requirements?
Closed-loop programs face fewer regulatory hurdles but offer limited acceptance. Open-loop programs require compliance with payment network rules, PCI DSS standards, and often money transmitter licenses.
- What percentage of loaded funds typically go unredeemed (breakage)?
Breakage rates vary by industry and program design, typically ranging from 5-20%. Sports venues and entertainment generally see higher redemption rates than retail or corporate programs.
- Can prepaid programs integrate with existing loyalty systems?
Yes, modern prepaid platforms support API integration with CRM and loyalty systems, enabling unified customer profiles and cross-program benefits.
The Next Phase of Payment Infrastructure
The evolution of payment systems has introduced innovative solutions to address persistent challenges in modern commerce. Reverse ATM and cash to card technology represents a sophisticated approach to bridging the gap between traditional cash transactions and digital payment ecosystems.
This guide explores the architecture, capabilities, and strategic applications of reverse ATM systems—tools that enable businesses to operate cashless environments while maintaining accessibility for customers who rely on cash.
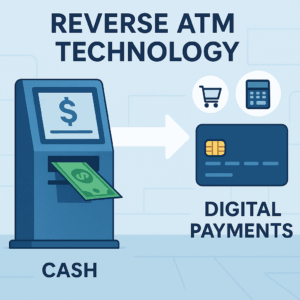 Defining Reverse ATM Technology
Defining Reverse ATM Technology
Reverse ATMs function as the inverse of traditional ATMs. Instead of dispensing cash from digital accounts, they accept cash deposits and issue digital payment credentials.
The term "reverse ATM" encompasses several implementations:
- Cash-to-card kiosks
- Cash exchange stations
- Automated currency conversion systems
All share a common purpose: converting physical currency into immediately usable digital instruments within controlled environments.
Modern systems extend beyond basic conversion. They frequently include:
- Account management features
- Balance inquiries and transaction histories
- Reload and reissue capabilities
These features transform reverse ATMs from single-purpose converters into full-featured payment terminals, combining the efficiency of cashless operations with inclusivity for cash-preferring users.
Technical Architecture and System Components
Reverse ATMs and cash to card solutions integrate multiple subsystems that coordinate to deliver reliable, secure functionality.
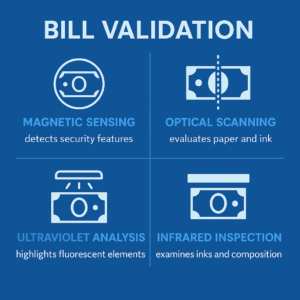
Bill Validation
The first stage of any transaction is authenticating the deposited cash. Modern bill acceptors use multiple technologies simultaneously:
- Magnetic sensing
- Optical scanning
- Ultraviolet and infrared analysis
Together, these achieve 99.9%+ accuracy while maintaining high processing speed, rejecting counterfeit or damaged bills before storage.
Secure Cash Storage
Validated currency is transferred into reinforced storage compartments featuring:
- Hardened materials and locking systems
- Tamper-evident seals
- Sensors that track capacity and trigger collection alerts
This layered approach ensures physical protection and precise reconciliation of funds.
Card Dispensing
The transaction concludes when a prepaid card is issued, encoded with the deposited value. Dispensing mechanisms are engineered for reliability, with sensors verifying encoding success before release. This minimizes service interruptions, even under high throughput.
Software Architecture and Transaction Processing
While the hardware provides the visible interface, software orchestrates the transaction flow.
Core functions include:
- Account creation and balance allocation
- Fraud detection and real-time authorization
- Integration with POS infrastructure
Real-time communication protocols ensure immediate activation and balance availability. Systems maintain data consistency across terminals—even during temporary outages—through automatic offline reconciliation. Modern platforms support multiple integration methods, from RESTful APIs to legacy protocols, allowing operators to implement reverse ATMs without replacing existing infrastructure.
 Advanced Bill Validation Technology
Advanced Bill Validation Technology
As counterfeiting grows more sophisticated, multi-spectral imaging has become the industry standard. By capturing bill characteristics across visible, ultraviolet, and infrared wavelengths, systems create unique digital "signatures" for each note. Machine learning algorithms enhance detection by identifying subtle anomalies and improving with each transaction. Systems also assess the physical condition of bills, rejecting those too damaged for storage or bank processing. International deployments may add multi-currency functionality, managing validation and conversion with separate storage compartments and exchange-rate logic.
Security Architecture and Threat Mitigation
Reverse ATMs must defend against both physical and digital threats.
Physical Security
- Hardened enclosures and anchoring systems
- Tamper sensors and intrusion alerts
Cybersecurity
- End-to-end encryption (in transit and at rest)
- Compliance with NIST standards for encryption and key management
- Secure network communications via VPN tunneling and intrusion detection
- Automated containment to isolate compromised nodes
This defense-in-depth model ensures operational integrity and customer trust.
Transaction Speed and Throughput
Customer satisfaction depends on speed and reliability. Advanced systems complete transactions—from bill insertion to card issuance—in under 30 seconds.
Key performance characteristics:
- High-speed validators processing multiple bills per second
- Parallel processing during validation and storage
- Optimized dispensing mechanisms with jam detection
- In-memory databases and distributed architectures to reduce latency
The result: thousands of concurrent transactions with consistent performance, even during peak usage.
User Interface Design and Accessibility
Interface design determines how easily customers adopt new systems. Effective reverse ATMs emphasize clarity, accessibility, and inclusivity through:
- Large, high-contrast touchscreen layouts
- Simple, step-by-step guidance
- Multilingual and visual prompts
- ADA-compliant accessibility features (audio guidance, tactile feedback, screen-reader compatibility)
By incorporating these principles, operators expand usability and comply with accessibility standards while improving the customer experience.
Technical FAQ
What security standards must reverse ATMs meet?
PCI DSS: Required for systems processing or transmitting cardholder data.
NIST Guidelines: Provide robust encryption and key-management frameworks.
AML/KYC: Transaction monitoring and suspicious-activity flagging to ensure compliance with anti-money-laundering laws.
How do multi-spectral bill validators achieve 99.9% accuracy?
Through sensor fusion and algorithmic cross-validation across multiple light spectrums:
- Visible light checks print quality and watermarks.
- UV light reveals fluorescent inks and strips.
- IR light analyzes magnetic and ink properties.
Hundreds of data points are verified against secure, continually updated databases.
What's the technical difference between magnetic stripe and EMV chip encoding?
| Feature |
Magnetic Stripe |
EMV Chip |
| Data Storage |
Static, linear tracks |
Encrypted, dynamic chip memory |
| Security |
Static—susceptible to cloning |
Dynamic—unique cryptogram per transaction |
| Fraud Risk |
Higher |
Significantly reduced |
Performance Analytics and Business Intelligence
Each transaction generates valuable operational and behavioral data.
- Transaction volumes → identify peak periods and staffing needs
- Customer behavior → reveal deposit size, usage frequency, and reload patterns
- System reliability metrics → track uptime, success rates, and processing times
These data streams form the foundation for continuous optimization, guiding decision-making, cost control, and customer-experience improvements.
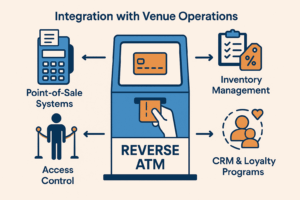 Integration with Venue Operations
Integration with Venue Operations
Cash to card kiosks deliver maximum value when integrated into venue ecosystems.
Basic integrations:
- POS and payment terminal compatibility
Advanced integrations:
- CRM and loyalty systems for personalized offers
- Access control systems (e.g., gates, lockers, or amenities)
- Inventory management for event or retail venues
This connectivity transforms reverse ATMs into strategic customer engagement tools, not just transactional utilities.
Maintenance and Reliability
Uptime is critical. Maintenance programs emphasize proactive reliability engineering:
- Preventive maintenance based on component lifecycles
- Remote diagnostics and predictive analytics
- Tiered firmware updates with rollback options
- Spare-parts management to balance availability and cost
Together, these practices sustain consistent service quality across large deployments.
Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management
Reverse ATMs intersect with multiple financial and consumer protection frameworks:
- Money transmission laws (jurisdiction dependent)
- AML/KYC requirements for transaction monitoring
- Consumer protection for fee transparency and dispute resolution
Designing systems with compliance in mind not only avoids legal risk but also builds customer confidence in system integrity.
Emerging Technologies and Future Developments
The reverse ATM and cash to card sector continues to evolve through innovation and convergence:
- Blockchain integration for immutable transaction records
- Biometric authentication to replace physical cards
- AI-driven fraud detection and predictive maintenance
- Mobile wallet integration enabling digital card issuance via app
These advances align reverse ATMs with omnichannel payment strategies, unifying physical and digital experiences.
Industry Applications
Reverse ATMs are already proving value across industries:
- Entertainment Venues & Stadiums: Accelerate concession sales during peak times
- Transit Systems: Reduce fare-collection costs while serving unbanked riders
- Universities: Integrate with student ID systems for dining and retail
- Corporate Campuses: Enable cashless cafeterias via employee badges
These case studies illustrate the technology's versatility and measurable operational benefits.
Strategic Implementation
Successful deployment requires strategic planning and change management:
- Define requirements (transaction volume, integrations, security).
- Pilot programs to validate assumptions and optimize workflows.
- Staff training for support and customer guidance.
- Awareness campaigns to encourage adoption and address concerns.
- Feedback loops for continuous improvement post-launch.
This structured approach maximizes both ROI and customer satisfaction.
Technical Specifications and Standards Appendix
Compliance Framework
Payment Card Industry Standards
- PCI DSS v4.0 compliance for cardholder data protection
- PA-DSS validation for payment applications
- P2PE certification for point-to-point encryption
Federal Standards and Guidelines
- NIST SP 800-57 Part 1 Rev. 5: Key Management Framework
- NIST Cybersecurity Framework v1.1: Core security functions
- FIPS 140-2 Level 3: Cryptographic module standards
- AES-256 encryption for data at rest and in transit
Financial Regulatory Compliance
- BSA/AML compliance for transaction monitoring
- FinCEN guidance on money transmission (varies by jurisdiction)
- Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) regulations
- State money transmitter licensing requirements
Performance Benchmarks
Transaction Processing
- Bill validation: <3 seconds per note
- Card encoding and dispensing: <10 seconds
- Complete transaction cycle: <30 seconds
- System throughput: 120+ transactions/hour (sustained)
- Uptime requirement: 99.5% availability
Security Metrics
- Counterfeit detection rate: >99.9%
- False positive rate: <0.1%
- Encryption strength: AES-256 with RSA-4096 key exchange
- Tamper detection response: <5 seconds
Hardware Specifications
- Bill acceptor capacity: 500-2,000 notes (model dependent)
- Card dispenser capacity: 100-500 cards
- Environmental operating range: 32°F to 104°F (0°C to 40°C)
- Network connectivity: Ethernet, Wi-Fi 802.11ac, cellular backup
Regulatory Framework Matrix
| Jurisdiction |
Money Transmission License |
Transaction Limits |
Reporting Requirements |
| Federal (US) |
MSB registration if >$1,000/day |
Varies by state |
CTR for >$10,000 |
| California |
Required for stored value |
No daily limits |
Monthly reconciliation |
| New York |
BitLicense for virtual currency |
$5,000/day individual |
Real-time monitoring |
| European Union |
EMD2 compliance |
€250 anonymous limit |
AMLD5 reporting |
Integration Standards
API Specifications
- RESTful API with JSON formatting
- OAuth 2.0 authentication
- Webhook support for real-time notifications
- Rate limiting: 1,000 requests/minute
POS Integration Protocols
- ISO 8583 messaging standard
- EMV L2 certification
- Contactless payment support (NFC, RFID)
- Legacy magnetic stripe compatibility
Data Exchange Formats
- Transaction logs: ISO 20022 XML standard
- Settlement files: NACHA ACH formatting
- Audit trails: SIEM-compatible CEF format
Conclusion
Reverse ATM technology has become essential infrastructure for organizations seeking to combine the efficiency of cashless operations with the inclusivity of cash-accepting services. By uniting advanced hardware, intelligent software, and robust security architecture, these systems deliver measurable operational and customer-experience value. As payment ecosystems evolve, these cash to card kiosks will remain cornerstone tools—bridging the physical and digital worlds of modern commerce.
The landscape of payment processing has undergone dramatic transformation over the past decade. From the early days of magnetic stripe cards to today’s contactless systems, businesses have continuously adapted to meet changing consumer expectations while managing operational complexity.
Among the most significant developments in this evolution is the emergence of cash-to-card and reverse ATM technology, which bridges the gap between traditional cash transactions and modern digital payment systems.
 Understanding the Modern Payment Ecosystem
Understanding the Modern Payment Ecosystem
Today’s payment environment is a hybrid of legacy and modern systems. Traditional point-of-sale platforms process credit and debit cards, while newer solutions incorporate mobile wallets, QR codes, and contactless transactions. Despite this technological progress, cash remains relevant for millions of consumers. Federal Reserve data shows that cash transactions still account for a substantial portion of retail purchases, especially among certain demographics and regions. This creates friction for businesses pursuing fully cashless models: how to reap the benefits of digital transactions without excluding cash-preferring customers.
Business outcome: To stay inclusive while modernizing, operators need solutions that serve both digital-first and cash-reliant customers.
The Rise of Cashless Payment Solutions
Cashless payment models gained traction as businesses sought to reduce costs, mitigate theft, and speed up transactions. Early versions focused narrowly on card acceptance, but today’s ecosystems are far more sophisticated, capable of supporting multiple payment types securely and efficiently.
The benefits extend well beyond convenience. Cashless operations lower labor and security expenses associated with handling cash, reduce theft vulnerability, accelerate transaction times, and generate actionable data for analytics. These advantages explain their adoption across retail, hospitality, transportation, and entertainment. Yet, fully eliminating cash carries risk. Customers who prefer or rely on cash may feel excluded, leading to lost revenue or reputational harm. Hybrid approaches emerged as the solution — keeping the efficiency of digital transactions while accommodating cash users through cash-to-card technology.
Cash-to-Card Technology: The Bridge Solution
Cash-to-card systems address the key challenge of going cashless: how to maintain operational efficiency while still serving customers who only carry cash. Rather than rejecting cash outright, these kiosks convert currency into prepaid digital value. Customers deposit cash, receive a prepaid card or digital credit in equivalent value, and can immediately spend it throughout the venue. Conversion happens in seconds, keeping lines moving. The resulting cards behave like debit cards within the venue’s ecosystem, offering customers a seamless experience while freeing businesses from the burden of cash handling. Modern systems are built with multiple layers of protection — encrypted transaction processing, secure cash storage, real-time monitoring, and full audit trails — meeting or exceeding banking standards. Venues gain all the benefits of going cashless — speed, security, analytics — without excluding cash-based customers.
Technical Architecture and Implementation
Cash-to-card kiosks combine hardware and software into a unified system.
- Bill acceptors use advanced validation to authenticate currency and reject counterfeits.
- Secure storage modules safeguard deposited funds while maintaining accurate inventory.
- Card dispensers encode and deliver prepaid cards reliably, even under heavy use.
On the software side, transaction engines manage account creation, balance allocation, and POS integration. Real-time communication ensures immediate card activation across all venue terminals. Connectivity enables remote monitoring and analytics dashboards that track transaction volumes, peak usage times, and system health — data that supports both day-to-day management and strategic planning. Robust architecture ensures reliability, protects revenue, and generates insights that cash handling cannot.
Integration with Existing Payment Infrastructure
Cash-to-card kiosks must function as part of the broader payment environment. Integration with point-of-sale systems ensures prepaid cards are accepted immediately across all terminals, with no difference in user experience. This typically involves API connections between the kiosks and payment processors, supporting functions like account creation, balance inquiries, and settlement. Standardized protocols make systems compatible with a wide range of existing POS hardware and software. Advanced implementations add value through branded card customization, loyalty program tie-ins, and promotional bonuses, turning the kiosks into marketing tools as well as payment infrastructure. Seamless integration reduces friction, strengthens customer experience, and creates opportunities for brand engagement.
Operational Benefits and Business Impact
 The operational improvements are immediate and measurable. By automating cash acceptance, venues reduce labor costs, shrink theft risk, and eliminate time spent reconciling tills and transporting deposits. Transaction speeds increase because digital payments process faster than cash exchanges. This boosts throughput during peak periods, enabling more sales without adding staff. Customers benefit from shorter lines and smoother experiences. Data capture is another advantage. Cash-to-card transactions generate detailed insights into spending behavior, supporting smarter inventory, staffing, and marketing decisions. Over time, operators also see reduced banking fees, more accurate reporting, and stronger financial controls. Venues achieve cost savings, faster service, better customer satisfaction, and improved decision-making.
The operational improvements are immediate and measurable. By automating cash acceptance, venues reduce labor costs, shrink theft risk, and eliminate time spent reconciling tills and transporting deposits. Transaction speeds increase because digital payments process faster than cash exchanges. This boosts throughput during peak periods, enabling more sales without adding staff. Customers benefit from shorter lines and smoother experiences. Data capture is another advantage. Cash-to-card transactions generate detailed insights into spending behavior, supporting smarter inventory, staffing, and marketing decisions. Over time, operators also see reduced banking fees, more accurate reporting, and stronger financial controls. Venues achieve cost savings, faster service, better customer satisfaction, and improved decision-making.
Security and Compliance Considerations
Because they handle both cash and digital value, cash-to-card systems must meet stringent security standards. Encryption protects transaction data in transit and at rest. PCI DSS compliance ensures cardholder information is handled properly. Tamper-evident housings, secure mounts, and surveillance integration protect physical hardware. Regulatory requirements vary by jurisdiction but often include money transmission licensing, consumer protection laws, and financial reporting obligations. Many systems now embed compliance tools to simplify operator responsibilities. Strong security and compliance frameworks protect both customer trust and operator liability.
Customer Experience and Adoption
Technology only succeeds if customers use it. Cash-to-card adoption hinges on intuitive design and strong education. Interfaces must be simple, with clear instructions, progress indicators, and multi-language options. Customers should be able to complete conversions in under ten seconds, with immediate activation confirming success. Education is equally important. Staff training, in-venue signage, and promotional campaigns help first-time users understand the process. Venues that actively promote and assist see significantly higher adoption. Simple, fast, and well-communicated systems build customer trust and drive repeat use.
Industry Applications and Use Cases
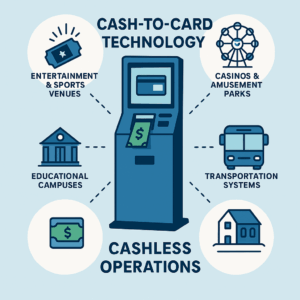 Cash-to-card technology is proving valuable across industries and use cases:
Cash-to-card technology is proving valuable across industries and use cases:
- Entertainment and sports venues accelerate concession sales while reducing theft risk.
- Casinos and amusement parks support customers who prefer cash while streamlining internal operations.
- Transportation systems modernize fare collection for riders without cards.
- Educational campuses enable students and visitors to use prepaid cards for dining and services.
- Festivals and pop-up events rely on portable systems to stay cashless in temporary settings.
Each environment configures the system differently, but the principle is the same: maintain the advantages of cashless operations without excluding cash-using customers.
Future Developments and Market Trends
The reverse atm and cashless payment market is advancing quickly. Mobile integration now allows customers to manage balances and reload cards via smartphone apps. Loyalty programs tie spending to rewards, encouraging ongoing usage. Artificial intelligence is being deployed for fraud detection, predictive maintenance, and usage forecasting. Cloud-based platforms are reducing the need for on-site infrastructure while improving scalability. Sustainability goals are shaping energy-efficient kiosk designs and reduced material use. Continuous innovation ensures cash-to-card systems remain relevant, adaptable, and aligned with evolving customer expectations.
Selecting the Right Cash-to-Card Solution
Operators evaluating solutions should weigh several factors:
- Transaction volume capacity relative to peak demand.
- Integration compatibility with current POS and payment processors.
- Security and compliance support for jurisdictional requirements.
- Long-term service, maintenance, and vendor support.
- Transparent cost models that account for both upfront investment and ongoing fees.
Careful vendor evaluation protects ROI and ensures system longevity. Asking the right questions can mean the difference between a successful deployment and an expensive, time consuming mistake.
Implementation Best Practices
Successful rollouts depend on planning. Site assessments identify optimal kiosk placement for visibility and flow. Staff training ensures smooth customer support. Marketing campaigns prepare customers for the change. Phased rollouts allow time for optimization and customer feedback. Regular maintenance schedules preserve reliability, while continuous monitoring ensures systems stay aligned with customer needs. A methodical, customer-focused implementation maximizes adoption and minimizes disruption.
Conclusion
Cash-to-card technology represents the practical bridge between cash and digital transactions. By converting physical currency into usable digital value, these systems allow businesses to enjoy the efficiencies of cashless operations without excluding cash-reliant customers. The technology delivers measurable benefits: reduced costs, faster service, improved customer satisfaction, and richer analytics. With innovations in mobile, AI, and cloud infrastructure, cash-to-card is positioned to expand its role in the evolving payment landscape. For operators, adopting cash-to-card today is not just about keeping up with technology — it’s about creating inclusive, efficient, and future-ready payment ecosystems.
Cashless Payment Solution FAQ
- How quickly can customers convert cash to a prepaid card?
Most modern cash-to-card kiosks complete transactions in about 30 seconds. Customers insert cash, receive their prepaid card, and can use it immediately at any point-of-sale terminal in the venue.
- What percentage of cash customers actually use these kiosks?
Adoption rates typically range from 15-30% in the first few months, increasing over time as customers become familiar with the process. Proper placement and staff education significantly impact these numbers.
- Can venues customize the prepaid cards with their own branding?
Yes, most systems offer full card customization including logos, colors, and messaging. Custom branded cards also serve as marketing tools that customers may keep as souvenirs.
- What happens if the kiosk runs out of prepaid cards?
Systems include remote monitoring that alerts operators before supplies run low. Many venues maintain backup card inventory and establish restocking schedules based on usage patterns.
- Do cash-to-card systems work if internet connectivity is interrupted?
Basic kiosk functions can operate offline for short periods, but card activation and POS integration require network connectivity. Most systems include backup communication methods to minimize disruption.
- Are there fees for converting cash to prepaid cards?
Fee structures vary by venue and local regulations. Some operators absorb costs as part of their cashless strategy, while others may charge small convenience fees. Transparent fee disclosure is standard practice.
Modern payment ecosystems increasingly demand solutions that balance operational efficiency with customer accessibility. Cash-to-card kiosks (also known as reverse ATMs) have emerged as strategic infrastructure that enables businesses to transition to cashless environments while continuing to serve customers who prefer or rely on cash. This guide examines the technical, operational, and strategic considerations business owners should evaluate to ensure successful implementation.
What is Cash-to-Card Technology?
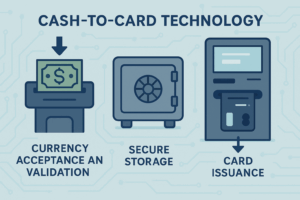 Core Architecture
Core Architecture
At their foundation, cash-to-card kiosks represent the integration of hardware and software designed to convert physical currency into digital payment credentials. The technology typically involves three critical components working in sequence:
- Currency acceptance and validation – High-accuracy bill acceptors verify currency authenticity using optical scanning, magnetic sensing, and counterfeit detection methods.
- Secure storage – Validated funds are placed into tamper-resistant storage with multiple layers of protection and audit trails to ensure both physical security and financial reconciliation.
- Card issuance – Prepaid cards, often branded for the venue or merchant, are encoded with equivalent value and activated instantly for use.
Touchscreen interfaces, intuitive prompts, and real-time confirmations help guide customers through the process with minimal friction.
Software and Payment Integration
The software layer is as important as the hardware, because it governs everything from transaction speed to compliance. These systems:
- Manage account creation, card activation, and balance tracking.
- Provide real-time communication to ensure funds are available immediately at point-of-sale terminals.
- Detect potential fraud by monitoring transaction patterns.
- Integrate with payment processors and POS systems to ensure compatibility and compliance with industry standards.
Analytics platforms are often embedded to give operators insight into usage patterns, transaction volumes, and system performance. This data supports both operational management and long-term planning.
How to Perform Deployment Planning and Site Assessment for Reverse ATMs and Cash to Card Kiosks
Location Strategy
Selecting where to place kiosks can determine the success of implementation. High-traffic, visible areas — near entrances, ticketing lines, or concession areas — maximize adoption. Placement should reduce bottlenecks and customer confusion, while remaining easily accessible to staff for monitoring and servicing (for more on optimal deployment locations, see our guide on the 8 uses for cash-to-card kiosks and specific implementation strategies for sports arenas and stadiums).
Infrastructure Requirements
Kiosks require reliable access to both electricity and network connectivity. Physical space should allow for comfortable customer interaction without obstructing traffic flow. Compliance with accessibility regulations such as ADA standards ensures that all customers can complete transactions independently.
Security Considerations
Deployment must also account for customer safety and operational risk. Clear sightlines, adequate lighting, and video surveillance integration all strengthen security. Placement decisions should balance convenience with protection against misuse or tampering. For a comprehensive overview of deployment best practices, see our complete guide to cash-to-card kiosk deployment.
Optimizing Transaction Flow and User Experience
The customer journey through a kiosk must be seamless. Intuitive interface design, combined with clear language and visual prompts, reduces confusion and shortens transaction times. Multi-language support is increasingly standard, reflecting the diverse populations that use these systems. Branding options, such as customized interfaces or kiosk wraps, allow businesses to reinforce their identity while still ensuring clarity. The most critical moment is card dispensing. Users must feel confident that the process is complete, with clear instructions to remove the card and immediate confirmation that funds are available. This reassurance directly impacts adoption and repeat use.
 Security and Fraud Prevention
Security and Fraud Prevention
Because kiosks handle both cash and digital payments, robust security is essential. Systems are typically designed with:
- Encryption protocols that secure customer data from the point of entry to activation.
- Compliance with PCI DSS to ensure proper handling of cardholder data.
- Fraud detection systems that flag unusual patterns for review.
- Advanced bill validation that identifies and rejects counterfeit or damaged currency.
These layers work together to protect both the business and the customer, building trust in the system.
Understanding Operational Management and Maintenance
Successful kiosk operations depend on consistent management practices. Routine responsibilities include:
- Cash collection – Balancing collection frequency with security and operational efficiency.
- Preventive maintenance – Scheduled servicing reduces downtime and prolongs equipment life.
- Inventory management – Monitoring prepaid card stock and ensuring timely restocking.
- Remote monitoring – Many systems allow operators to identify issues before they affect customers, such as low card supplies or connectivity disruptions.
Together, these practices maintain uptime, protect revenue, and preserve customer trust.
Financial Modeling and ROI
Understanding the key benefits of reverse ATMs helps frame the ROI discussion and business case. Evaluating the business case for cash-to-card kiosks requires balancing costs against both tangible and intangible returns.
Cost advantages come from reduced cash handling, lower risk of theft or loss, and labor savings. By moving cash transactions into automated systems, staff resources can be redeployed to revenue-generating tasks. Faster transaction processing also reduces lines and increases throughput during peak times.
Revenue opportunities may emerge through higher overall spending once customers transition to card-based payments, as well as through potential surcharges or convenience fees depending on the regulatory environment.
Break-even analysis should incorporate transaction volume, average load size, installation and service costs, and labor savings. Transparent fee structures — whether flat service agreements or revenue-sharing — are critical to accurately modeling return on investment.
 How to use Reverse ATMs for Marketing and Customer Engagement
How to use Reverse ATMs for Marketing and Customer Engagement
Kiosks can also extend beyond pure payment infrastructure. Many operators leverage them as marketing tools:
- Branded cards reinforce customer loyalty and create ongoing visibility outside the venue.
- On-screen promotions allow targeted advertising during the transaction process.
- Receipt-based offers can promote events, loyalty programs, or special discounts.
When strategically integrated, these features turn kiosks into dual-purpose assets that support both payment and marketing objectives.
Vendor Evaluation and Selection
While specific features vary, several criteria consistently define strong kiosk partners:
- Industry experience and a track record of successful deployments.
- Compliance certifications (e.g., ISO 9001:2015, PCI DSS) demonstrating adherence to standards.
- Support infrastructure, including technical assistance, service-level agreements, and maintenance capabilities.
- Pricing transparency, so decision-makers understand the total cost of ownership without hidden fees.
The right vendor should demonstrate both technical competence and an ability to align with the business’s long-term operational and strategic goals. For more guidance on evaluating vendors, see our article answering common questions about cash-to-card kiosks.
Conclusion
Cash-to-card kiosks are no longer experimental — they are becoming a standard bridge between cash-dependent customers and increasingly cashless environments. Their value lies in creating operational efficiency, reducing risks, and supporting better customer experiences, all while positioning businesses for future-ready payment ecosystems.
When implemented thoughtfully — with careful attention to technology, security, deployment strategy, and vendor partnerships — cash-to-card kiosks can deliver measurable ROI and become a cornerstone of modern payment infrastructure. Interested in learning more about where this technology is heading? Explore more with our guide to future trends in cashless payment technologies!
Cash to Card and Reverse ATM Implementation FAQ
How much does it typically cost to implement cash-to-card kiosks?
Implementation costs vary based on kiosk specifications, transaction volume, and service agreements. Most vendors offer either flat-rate service agreements or revenue-sharing models. Contact us for a customized quote based on your specific requirements.
How long does installation and setup typically take?
Standard installation usually takes 1-2 days per kiosk, including network setup, testing, and staff training. Larger deployments may require additional coordination time.
What happens if the kiosk runs out of cards or breaks down?
Modern systems include remote monitoring that alerts operators before supplies run low. Most service agreements include response time guarantees for technical issues, with backup procedures to minimize customer impact.
Do customers actually use these kiosks, or do they just ignore them?
Adoption rates vary by venue type and customer demographics, but proper placement and clear signage typically result in steady usage. Many operators see a substantial number of cash customers transitioning to kiosk use within the first few months.
Can we set our own fees or card loading limits?
Fee structures depend on your service agreement and local regulations. Card loading limits can usually be customized based on your average transaction sizes and risk tolerance.
The modern consumer has spoken, and their message is clear: they want control, convenience, and speed. Across every industry, from retail and hospitality to healthcare and government services, customers are increasingly gravitating toward self-service options that put them in the driver's seat of their experience.
This shift isn't just a trend—it's a fundamental transformation in how people prefer to interact with businesses. Understanding and adapting to this change has become essential for organizations looking to meet customer expectations and remain competitive in today's digital landscape.
The Forces Driving Self-Service Adoption
 Several converging factors have accelerated the demand for self-service solutions across industries.
Several converging factors have accelerated the demand for self-service solutions across industries.
Digital Native Expectations: Today's consumers, particularly millennials and Gen Z, have grown up with smartphones, apps, and instant access to information. They expect the same level of immediacy and control in their offline interactions that they experience online. For these digital natives, waiting in line for a human representative often feels unnecessary and inefficient.
The Pandemic Effect: COVID-19 dramatically accelerated self-service adoption by making contactless interactions not just convenient, but necessary. What began as a health precaution quickly revealed the efficiency benefits of self-service options. Many customers discovered they preferred the speed and autonomy these solutions provided, creating lasting behavioral changes that persist well beyond pandemic restrictions.
24/7 Availability Demands: Modern life doesn't operate within traditional business hours. Customers want to access services when it's convenient for them—whether that's 6 AM before work or 10 PM after putting the kids to bed. Self-service kiosks and automated systems provide round-the-clock availability that human-staffed operations simply can't match cost-effectively.
Personalization and Privacy: Self-service options often allow customers to take their time, review options thoroughly, and make decisions without feeling rushed or judged. This is particularly valuable in sensitive situations, such as healthcare check-ins or financial transactions, where privacy and discretion are important.
Self-Service Across Industries
The adoption of self-service technologies spans virtually every sector, each finding unique ways to enhance customer experience while improving operational efficiency.
Retail and Quick Service: Grocery stores have embraced self-checkout stations, while fast-food chains use ordering kiosks to reduce wait times and increase order accuracy. These solutions allow customers to browse menus at their own pace, customize orders precisely, and avoid miscommunication that can occur with verbal orders.
Healthcare: Patient check-in kiosks have revolutionized waiting room experiences, allowing patients to verify information, update insurance details, and complete forms digitally. This reduces administrative burden on staff while giving patients more control over their visit preparation.
Hospitality and Travel: Hotels offer self-service check-in kiosks that eliminate front desk queues, while airports deploy numerous self-service options for check-in, baggage tagging, and security document verification. These solutions are particularly valuable in high-volume environments where speed and efficiency are paramount.
Government Services: Municipal offices and DMV locations increasingly rely on self-service kiosks for routine transactions like permit renewals, fee payments, and information requests. This allows government workers to focus on complex cases that require human intervention while providing citizens with faster service for standard requests.
Entertainment and Events: Movie theaters, theme parks, and sports venues use self-service kiosks for ticket purchases, concession orders, and merchandise sales. These systems reduce staffing needs during peak times while eliminating bottlenecks that can negatively impact the customer experience.
The Business Benefits of Self-Service
 Organizations implementing self-service solutions report significant advantages beyond improved customer satisfaction.
Organizations implementing self-service solutions report significant advantages beyond improved customer satisfaction.
Operational Efficiency: Self-service kiosks can handle multiple transactions simultaneously without breaks, sick days, or varying service speeds. This consistency allows businesses to maintain service levels even during staff shortages or peak demand periods.
Cost Reduction: While the initial investment in self-service technology requires capital, the long-term savings in labor costs can be substantial. Staff can be redeployed to higher-value activities that require human expertise and creativity.
Data Collection and Analytics: Digital self-service interactions generate valuable data about customer preferences, peak usage times, and common service requests. This information enables businesses to optimize operations and make data-driven decisions about service offerings.
Scalability: Self-service solutions can handle volume fluctuations more easily than human-staffed operations. During busy periods, customers can use multiple kiosks simultaneously, while slower periods don't result in idle labor costs.
Overcoming Implementation Challenges
Despite the clear benefits, organizations must navigate several challenges when implementing self-service solutions.
User Experience Design: The interface must be intuitive enough for users of all ages and technical abilities. Poor design can create frustration and drive customers away from self-service options entirely. Successful implementations prioritize simplicity, clear navigation, and accessibility features.
Technology Integration: Self-service kiosks must integrate seamlessly with existing systems, from payment processors to inventory management and customer databases. This requires careful planning and often custom development to ensure smooth operation.
Maintenance and Support: Self-service systems require ongoing maintenance, software updates, and technical support. Organizations must plan for these operational requirements and have protocols in place for handling system outages or malfunctions.
Staff Training and Change Management: Employees need training on how to assist customers with self-service options and when to intervene. Managing the transition requires clear communication about how self-service enhances rather than replaces human jobs.
The Future of Self-Service
As technology continues to evolve, self-service solutions are becoming more sophisticated and capable of handling increasingly complex interactions.
 Artificial Intelligence Integration: AI-powered kiosks can provide more personalized recommendations, understand natural language queries, and learn from customer interactions to improve over time. This makes self-service options more helpful and engaging.
Artificial Intelligence Integration: AI-powered kiosks can provide more personalized recommendations, understand natural language queries, and learn from customer interactions to improve over time. This makes self-service options more helpful and engaging.
Biometric Authentication: Fingerprint scanners, facial recognition, and other biometric technologies are making self-service more secure while eliminating the need for cards, codes, or passwords.
IoT Connectivity: Internet of Things integration allows self-service kiosks to communicate with other systems and devices, enabling more comprehensive service offerings and better inventory management.
Mobile Integration: Customers increasingly expect to start transactions on their mobile devices and complete them at kiosks, or vice versa. This omnichannel approach provides maximum flexibility and convenience.
Meeting Customer Expectations
The rise of self-service reflects a broader shift in customer expectations around control, convenience, and efficiency. Businesses that recognize and adapt to this trend position themselves to deliver the experiences modern consumers demand.
However, successful self-service implementation isn't about replacing human interaction entirely—it's about providing customers with choices and using technology to enhance rather than diminish the overall service experience. The most effective approaches combine efficient self-service options with available human support when needed.
Organizations that embrace self-service solutions thoughtfully, with careful attention to user experience and integration with existing operations, will find themselves better equipped to meet evolving customer expectations while building more efficient and resilient business operations.
In our increasingly digital world, self-service isn't just an option—it's becoming an expectation. The businesses that thrive will be those that recognize this shift and implement solutions that truly serve their customers' desire for autonomy, speed, and convenience.
The definition of what makes a valuable customer interaction is expanding. While speed and efficiency remain important, a purely transactional encounter often misses the opportunity to build loyalty or leave a lasting positive impression. Businesses are increasingly seeking ways to make every touchpoint more meaningful, and the once-humble digital kiosk is emerging as a surprisingly powerful ally in this endeavor. No longer confined to simple order-taking or information retrieval, modern interactive kiosks are evolving into dynamic platforms designed to create richer, more engaging customer experiences.
At REDYREF, we've seen firsthand how this evolution can reshape customer perception and interaction. We believe the true strength of today’s kiosk technology lies in its capacity to move beyond the transaction, fostering genuine engagement and building stronger connections.

Crafting Experiences, Not Just Processing Orders
Modern interactive kiosks are versatile platforms capable of transforming how customers connect with a brand, access information, and navigate services. Here’s how they are making a difference:
- Personalized Journeys: Interactive kiosks can offer tailored experiences based on user input or loyalty program data. Imagine a retail kiosk suggesting outfits based on a customer's style quiz, or a hospitality kiosk remembering a guest's preferences for a quicker, more personalized check-in. This level of personalization makes customers feel understood and valued.
- Immersive Information and Discovery: Instead of static displays, kiosks can provide dynamic, rich content. Customers can explore product features in 3D, watch how-to videos, compare options side-by-side, or take virtual tours. In a complex environment like a large venue or campus, interactive wayfinding kiosks don’t just show a map; they guide users with intuitive, step-by-step directions and highlight points of interest, turning potential frustration into a seamless discovery process.
- Empowering Customers with Control and Convenience: Well-designed kiosks empower users by giving them control over their experience. Whether it's customizing an order at a restaurant, managing appointments, accessing account information, or self-service ticketing, customers appreciate the autonomy and efficiency. This isn't just about speed; it's about providing a convenient, user-friendly interface that makes their lives easier.
- Building Brand Connection and Storytelling: Kiosks offer a unique channel to reinforce brand identity and share your story. Through customized interfaces, engaging visuals, and interactive brand-related content, businesses can create a more profound connection with their audience. A museum kiosk can offer deeper dives into exhibits, or a corporate lobby kiosk can showcase company values and achievements, making the brand more tangible and relatable.
- Gathering Valuable Insights (Ethically): While providing engaging experiences, interactive kiosks can also gather valuable (and anonymous, if preferred) data on customer preferences, common queries, and interaction patterns. These insights can be instrumental in further refining services, optimizing offerings, and continuously improving the overall customer journey.
- Reducing Friction and Enhancing Staff Effectiveness: By handling routine inquiries or transactions, interactive kiosks can free up staff to focus on more complex, high-value customer interactions. This doesn’t replace the human element but enhances it, allowing employees to provide more specialized support where it’s needed most, leading to greater overall customer satisfaction.
The Future of Engagement is Interactive
The shift towards experiential customer engagement is undeniable. Interactive kiosks are at the forefront of this transformation, offering businesses innovative ways to captivate audiences, provide exceptional service, and build stronger brand affinity. It’s no longer about just getting through a transaction; it's about making every interaction an opportunity to impress, inform, and engage.
At REDYREF, we’re passionate about designing and manufacturing interactive kiosk solutions that help businesses unlock these experiential possibilities. We believe that with the right approach, a kiosk can be one of your most powerful tools for building lasting customer relationships.
The world of digital building directories is brimming with possibilities—static screens, rotating slides, interactive touchscreens, wall mounts, floor-standing kiosks, and even advanced features like 3D mapping or mobile integration. For businesses ready to move beyond outdated paper or strip directories, the sheer variety can feel overwhelming. Where do you even begin?

At REDYREF, we’ve helped countless clients navigate this decision, and we’ve learned that it all boils down to finding the right fit for your unique needs. To simplify the process, let’s break it down with a focus on two main options—touch vs. non-touch digital directories—and explore how the “three Ss” (Situation, Setting, and Surroundings) can guide your choice. Whether you’re outfitting an airport, a medical campus, or a high-rise apartment lobby, here’s what you need to know to make an informed decision.
Touch vs. Non-Touch: What’s the Difference?
First, the basics. Non-touch digital directories come in two flavors:
- Static: A fixed display showing consistent info, like office numbers or tenant locations.
- Rotating: A screen cycling through pre-set “slides” of information, with sections or the entire display updating automatically.
Touchscreen directories, on the other hand, bring interactivity to the table. These range from:
- Limited touch: Simple one- or two-button controls to page through screens or return to “home.”
- Fully interactive: Tablet-like capabilities with advanced software, enabling personalized wayfinding, searches, or custom features.
While touchscreens might seem like the obvious winner with their versatility, the best choice hinges on your specific environment. That’s where the “three Ss” come in.
The Three Ss: Your Decision-Making Framework
-
Situation: What’s the Purpose?
The “why” behind your directory shapes everything. If you’re an airport displaying flight info for hundreds of travelers at once, a large, non-touch rotating screen is ideal—readable from a distance, cost-effective, and no interactivity needed. Contrast that with a sprawling medical campus, where patients and visitors need tailored directions across multiple buildings. Here, smaller, full-touchscreen kiosks offering detailed interactive wayfinding outshine static displays by delivering a frustration-free, personalized experience.
Somewhere in between? Consider limited-touch options—like the headrest screens on airplanes. Passengers can page through entertainment options without needing full interactivity, balancing function and cost.
-
Setting: Where’s It Going?
The environment itself matters. A 40-floor apartment building in NYC might only need a compact touchscreen (under 26”) for tenants to scroll through names—basic yet effective. Add premium features like local maps or building announcements, and it’s still manageable. But a mixed-use development with shops, restaurants, and residences demands more: a fully interactive kiosk that lets users buy movie tickets, make reservations, or plan multi-stop routes.
For a hospital campus, ADA compliance and ease of use are non-negotiable. Patients—often stressed or short on time—benefit from touchscreen wayfinding that’s intuitive and calming, far beyond what a static floor-by-floor directory can offer.
-
Surroundings: Where’s It Placed?
Placement within the space seals the deal. A small office with 15 tenants can thrive with a wall-mounted, static non-touch directory—all the info fits on one screen, no bells or whistles required. Scale up to a larger facility with dozens of tenants or added functionality (like a digital receptionist), and a freestanding touchscreen kiosk becomes the smarter pick for accessibility and engagement.
In a staffed lobby, a desk-mount interactive directory can lighten the load on receptionists during peak hours, letting visitors self-serve while still having help nearby. For a high-rise apartment with 100+ residents, a floor-mounted unit with limited touch (scrolling and buzzing in guests) strikes the perfect balance.

Why It Matters—and Why REDYREF Excels
Choosing between touch and non-touch isn’t just about features; it’s about maximizing value for your business and your users. A poorly matched directory can frustrate customers, waste resources, or miss opportunities to impress. That’s why we at REDYREF emphasize careful planning around the “three Ss”—it’s the key to unlocking a solution that works today and scales tomorrow.
As an end-to-end manufacturer of self-service kiosks, we’ve deployed digital directories for every imaginable scenario—from sleek office lobbies to bustling airports. Our clients, including industry leaders like Hilton and AT&T, trust us to deliver best-in-class experiences backed by ISO 9001:2015-certified quality. Whether you need a simple static display or a fully immersive wayfinding hub, we’ve got the expertise to make it happen.
Ready to Find Your Perfect Fit?
Investing in a digital directory doesn’t have to be daunting. Start with the “three Ss,” and let REDYREF guide you the rest of the way. Submit a request for proposal online or call us at (800) 628-3603 today to explore how our interactive kiosk solutions can elevate your space—and your customer experience. The future of wayfinding is here—let’s build it together.
Endless Aisle. Omnichannel. Virtual Merchandising. Unified Commerce. These terms might sound like retail jargon, but they represent a fundamental shift in how we shop and how businesses operate. At REDYREF, we've been at the forefront of kiosk technology for over 100 years (yes, you read that right!), and we're seeing firsthand how these concepts are transforming the retail landscape. We've helped countless businesses navigate these changes, and we can help you too.

What's Driving the Shift to Retail Automation?
Let's face it, the retail industry is evolving faster than ever. Consumers are more connected and informed than ever before. They're no longer satisfied with a standard in-store experience. They expect seamless, personalized experiences that blend the physical and digital worlds. This is where retail automation, particularly through interactive kiosks, comes into play. Think of it this way: your customers are already living in a digitally-connected world – shouldn't your retail experience match that?
Key Concepts in Retail Automation: A Breakdown
Let's break down some of the key concepts shaping the future of retail (and we'll try to keep from getting too bogged down in technicalities):
- Endless Aisle: This kiosk strategy allows retailers to extend their in-store inventory virtually. Imagine a customer being able to browse your entire catalog, even if you don't have the physical space to display it all. Using in-store self-service kiosks, customers can browse and purchase products that aren't physically available on the shelves, often with options for home delivery or in-store pickup.
- Omnichannel: This approach focuses on creating a consistent brand experience across all channels – online, mobile, and in-store. It is about making sure your brand's message and look are the same everywhere a customer interacts with you. While important, it primarily focuses on marketing and merchandising, and not on fully integrating the tech you use.
- Virtual Merchandising: This involves using technology to enhance the in-store experience. We're talking about interactive elements that make shopping more engaging. Examples include virtual mannequins (interactive holograms), touch-on-glass displays (turning windows into touchscreens), and digital kiosks that connect customers with remote sales associates.
- Unified Commerce: This is the most advanced and integrated approach. It's the holy grail of modern retail. It goes beyond omnichannel by connecting not just the customer-facing channels but also the underlying infrastructure – POS systems, inventory management, customer data, and more. This creates a truly seamless experience where customers can shop, pay, and interact with the brand in any way they choose. It's about making every part of your business work together, seamlessly.
The Power of Unified Commerce: A Personalized Shopping Journey That Drives Sales
Imagine a customer browsing essential oils in a store. With a unified commerce system, powered by our technology, they could:
- Scan QR codes with their phone to learn about specific oils, their benefits, and related products, accessing a wealth of information beyond what a small label can provide.
- Add items to their digital cart directly from their phone, making shopping more convenient.
- Walk out of the store with their purchases, having paid through their mobile device, skipping the checkout line entirely.
- Alternatively, browse in-store, use a kiosk to order out-of-stock items for home delivery, and pay for everything at once, blending the physical and digital shopping experiences.
- Connect with a certified expert via video chat on a kiosk for personalized advice, getting the same level of service they'd expect from a dedicated in-store expert.
This level of personalization and convenience is what sets unified commerce apart, and it's what today's customers are starting to expect. It is not just about convenience, it is about creating a better experience that builds loyalty and boosts sales.
Automated Retail Kiosks: Beyond Vending Machines, Into True Customer Engagement
Automated retail kiosks are experiencing explosive growth, and for good reason. These aren't your typical vending machines. They're sophisticated, interactive systems capable of dispensing high-value products and providing personalized experiences. We're talking about kiosks that can sell anything from luxury cosmetics to electronics, and even cars!
Why are Major Brands Embracing Automated Retail? Here's the Inside Scoop
- Novelty and Attention: A car "vending machine" is a surefire way to generate buzz and attract attention. It's a talking point that gets people interested in your brand.
- Cost Optimization: In high-rent locations like airports, self-service retail kiosks offer a cost-effective way to establish a presence without the overhead of a full store. You can reach more customers in more places, without breaking the bank.
- Targeted Merchandising: Kiosks can be stocked with a curated selection of products tailored to the specific location and customer demographic. This means you can offer the right products to the right people at the right time -- even fresh food! -- maximizing your sales potential.
- 24/7 Availability: Kiosks don't need breaks! They can operate around the clock, extending your sales hours and catering to customers' busy schedules.

The Benefits of Retail Automation: Real Results You Can See
- Increased Sales: Endless aisle, virtual merchandising, and unified commerce strategies can lead to higher sales by offering more choices and a more convenient shopping experience. It's simple: make it easier for customers to buy, and they'll buy more.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Personalized interactions, seamless transactions, and on-demand assistance contribute to greater customer satisfaction. Happy customers become repeat customers, and that's good for business.
- Operational Efficiency: Automated retail kiosks can reduce labor costs and optimize inventory management. You can do more with less, freeing up your staff to focus on other important tasks.
- Valuable Data Insights: Interactive kiosks collect data on customer behavior, preferences, and purchasing patterns, providing valuable insights for marketing and merchandising. This data helps you understand your customers better, so you can make smarter decisions about your business.
REDYREF: Your Partner in Retail Automation
At REDYREF, we take pride in helping businesses leverage the power of interactive kiosks and digital technology to transform their retail operations. We offer a wide range of customizable kiosk solutions, suitable for applications from endless aisle and virtual merchandising to fully integrated unified commerce platforms. Our expertise spans design, engineering, manufacturing, and deployment, making us a one-stop shop for all your retail automation needs. We don't just sell kiosks; we build long-term partnerships. We take the time to understand your specific needs and goals, and we work closely with you to develop a solution that's tailored to your business. Our experience and track record of success with leading brands prove that we are a trusted authority in this field.
The Future of Retail is Here, and We're Here to Help Your Company Thrive
The lines between physical and digital retail are blurring. Consumers expect seamless, personalized experiences, and businesses that embrace retail automation will be best positioned to thrive in this evolving landscape. Don't get left behind!
Ready to explore how retail automation can benefit your business and take it to the next level? Give us a call at (800) 628-3603 ext 525 or submit a request for a proposal online. Our team of experienced professionals is here to guide you every step of the way, from initial concept to successful implementation. Let's shape the future of retail together.
While traditional printed, handwritten, or analog building directories still have a place in some spaces, the shift to digital directories and wayfinding solutions has gained significant traction over the past decade. With advancements in technology making these solutions more affordable, even small businesses are adopting digital directories to enhance the visitor experience and streamline operations.
If you’re considering making the switch, it’s natural to feel overwhelmed. A successful digital directory rollout requires thoughtful planning, from design and engineering to software development and deployment. But with the right partner, you can create a solution that meets the needs of both your business and your end users while avoiding common pitfalls.

Why Go Digital? The Key Benefits
1. Effortless Updates:
One of the biggest frustrations with traditional directories is the time and effort required to update them. Digital and interactive directories allow for real-time updates, ensuring information is always accurate and relevant.
2. Improved Accessibility:
Digital directories can integrate features like multilingual support, audio guidance, or enhanced visual clarity, making them more inclusive for all users, including those with disabilities.
3. Enhanced User Experience:
With interactive touchscreens and intuitive interfaces, digital directories provide an effortless way for visitors to find what they need quickly, whether it’s a specific office, department, or amenity.
4. Space for More Information:
Digital solutions can display more information than a static directory. From real-time event schedules to detailed interactive wayfinding maps, digital directories offer unmatched flexibility.
5. Branding Opportunities:
A sleek, modern digital directory reinforces your company’s brand image and can even display promotional content or advertising, creating additional revenue streams.
Choosing the Right Partner for Your Digital Directory
Selecting a partner to bring your digital directory to life is one of the most important decisions you’ll make in this process. Look for a provider with end-to-end capabilities, including design, engineering, fabrication, and directory and wayfinding software development. This vertical integration eliminates the need to juggle multiple vendors and minimizes the risk of miscommunication, saving both time and money.
A fully integrated partner, like REDYREF, simplifies project management by serving as a single point of contact. From initial concept to final deployment, every step is handled in-house, ensuring efficiency and accountability.

A Collaborative Process for a Tailored Solution
Before the design process even begins, your kiosk partner should work closely with you to understand the unique needs of your business and your users. Key questions might include:
•What are the main challenges with your current directory system?
•Are frequent updates causing delays or logistical issues?
•What specific information is most valuable to end users?
•How do users interact with the directory now, and what features would improve their experience?
This collaborative approach ensures that the final design is not only functional but also highly intuitive for users. The result? A solution that enhances the user experience while addressing your business challenges.
From Concept to Completion: The REDYREF Advantage
With REDYREF’s vertically integrated kiosk manufacturing process, your digital directory goes through every stage of development under one roof. Here’s what you can expect:
•Custom Design: A team of industrial designers and engineers works to create a solution tailored to your needs.
•Fabrication: Components are produced using state-of-the-art techniques, ensuring durability and precision.
•Finishing Touches: From powder coating to custom branding wraps, every detail is fine-tuned.
•Hardware Integration: Cutting-edge components like touchscreens, NFC payment systems, and printers can be seamlessly incorporated.
•Custom Software Development: REDYREF’s in-house team ensures your directory operates smoothly with features that align with your specific requirements.
•On-Site Installation: Your digital directory is delivered and installed, ready to enhance your space from day one.
Elevate Your Space with REDYREF Digital Directories
Switching to a digital directory doesn’t have to be a daunting process. By partnering with a team that can manage every aspect of the project, you can enjoy a streamlined experience that ensures a successful deployment.
Whether you’re a small business looking for a single directory or a large organization in need of a multi-location rollout, REDYREF has the expertise and resources to make it happen. Ready to bring your space into the future?
Contact us today to learn how REDYREF can transform your directory system into a modern, efficient, and user-friendly solution.
Let's talk about a challenge many businesses are facing: rising labor costs, particularly with mandated minimum wage increases in many states. It's a reality that's impacting bottom lines, especially in industries like retail and food service. But there's a solution gaining traction that can help mitigate these costs while also improving efficiency and customer satisfaction: automation through self-service kiosks.
Here at REDYREF, we've been at the forefront of digital kiosk technology for years. We've seen firsthand how automation can transform businesses, and we're here to tell you that it's not some futuristic concept – it's happening now, and it's more accessible than you might think.
Why is Automation Suddenly a Hot Topic?
Several factors are converging to make automation, particularly self-service kiosks, a critical consideration for businesses:
- Minimum Wage Hikes: The push for a $15 minimum wage, particularly for fast-food workers in places like New York, is a major catalyst. Businesses are realizing they need to find ways to offset these increased labor costs to stay profitable.
- Successful Early Adopters: Major brands like Starbucks and Panera have successfully implemented customer-driven ordering processes, demonstrating the viability and consumer acceptance of self-service.
- Technological Advancements: Rapid progress in areas like self-driving cars is making the public more comfortable with the idea of automation in everyday life.
- The Need to Control Labor Costs: Beyond wages, businesses are looking to minimize expenses associated with benefits, absenteeism, human error, and health and safety issues.
Who's Using Self-Service Kiosks? (Hint: It's Not Just Big Corporations)
You might be surprised at the wide range of businesses embracing kiosk technology. From major airports and hotel chains to universities, retail giants, and even "mom and pop" shops, self-service kiosks are proving their value across diverse industries.
Here are some common examples:
- Airport, University, and Business Directories: Touchscreen kiosks that help people find their way.
- Ticket Vending: For public transportation, sporting events, and entertainment venues.
- Restaurant Ordering: Self-service kiosks in fast-food and fast-casual restaurants.
- Tabletop Tablets: For ordering and payment at full-service restaurants.
- Hotel Check-In: Streamlining the check-in/check-out process at hotels.
When Does Automation Make Sense?
It's not just about busy times. While kiosks can certainly handle peak customer flow, they can also be incredibly useful in situations where staffing a location with full-time employees isn't cost-effective. Think of a library branch with lower traffic or an information desk in a less frequented part of a building.

Why Are Businesses Turning to Kiosks? The Real Reasons
The primary driver is cost control, especially concerning labor. But beyond that, there are compelling reasons to consider automation:
- Increased Efficiency: Kiosks can process orders and transactions faster than humans, reducing wait times and improving customer flow.
- Improved Accuracy: Automated systems minimize human error, leading to fewer mistakes in orders and transactions.
- Upselling and Cross-Selling: Kiosks can be programmed to suggest relevant add-on items, increasing average transaction value.
- Valuable Data Collection: Kiosks can gather data on customer preferences, traffic patterns, and popular items, providing valuable insights for business decisions.
Self-Service Kiosks: Not Just for the Big Guys
While large corporations were early adopters, interactive kiosk technology has become more affordable and accessible, making it a viable option for smaller businesses as well. In fact, these are the businesses that can see some of the biggest benefits, as they are often the hardest hit by the rising minimum wage increases.
Real-World Example: How Kiosks Can Transform a Small Business
Consider a small, locally-owned diner. By implementing self-service ordering kiosks, they could:
- Reduce labor costs: Potentially needing only one front-of-house employee instead of two, especially during slower periods.
- Increase table turn: Faster ordering and payment mean tables open up more quickly.
- Boost revenue: Even a modest increase in table turns can significantly impact annual revenue.
- Improve order accuracy: Fewer errors lead to happier customers and less wasted food.
The Retail Revolution: How Kiosks Are Changing the Game
Retail is another sector ripe for kiosk disruption. Here's how they're making a difference:
- Empowering Customers: Interactive directories help shoppers find what they need quickly and independently.
- Streamlining Checkout: Self-checkout kiosks reduce wait times, especially during peak hours.
- Expanding Inventory: In-store kiosks allow customers to order items not available on the shelves, shipped directly to their homes.
- Boosting Sales: Kiosks never forget to upsell or cross-sell, increasing average transaction value.
Addressing the Downsides: Smart Planning is Key
Of course, no technology is without its potential drawbacks. Early kiosk deployments were sometimes plagued by high maintenance costs and technical glitches. However, advancements in software and remote management capabilities have largely addressed these issues.
The most common reason for kiosk program failure? Inadequate planning and a lack of clear goals.
Here's how to avoid common pitfalls:
- Choose the Right Software: This is crucial for reliability and ease of maintenance. Modern kiosk software is designed to be robust and remotely manageable.
- Set Clear Goals: Define what you want your kiosk program to achieve from the outset. This will guide your decisions throughout the process.
- Thorough Research: Understand your target audience, their needs, and their comfort level with technology.
- Invest in User-Friendly Design: Make sure the kiosk interface is intuitive and easy to navigate.
The Bottom Line: Automation is Here to Stay
The shift towards automation is not a fad; it's a fundamental change in how businesses operate. By embracing self-service kiosk technology, companies can adapt to the evolving economic landscape, improve efficiency, and enhance the customer experience.
REDYREF: Your Partner in Automation
At REDYREF, we're here to help businesses thrive in the age of automation. As a provider of vertically integrated kiosk solutions, we offer a range of customizable options designed to meet your specific needs, all backed by our commitment to quality, reliability, and exceptional customer support. We have the experience and expertise to guide you through every step of the process, from initial concepting to deployment and ongoing maintenance.
Ready to explore how self-service kiosks can help your business navigate rising labor costs and achieve new levels of success? Simply submit a request for a proposal online or call (800) 628-3603 today for more information.

 The transition from cash-based to
The transition from cash-based to  Reliable infrastructure underpins every prepaid program. At the core,
Reliable infrastructure underpins every prepaid program. At the core,  Data Analytics and Business Intelligence
Data Analytics and Business Intelligence Custom prepaid card programs deliver strategic value that far exceeds payment processing. They reduce costs, accelerate transactions, enhance customer experience, and provide valuable business intelligence. Organizations considering implementation often have questions about deployment, which should be addressed early in the planning process.
Custom prepaid card programs deliver strategic value that far exceeds payment processing. They reduce costs, accelerate transactions, enhance customer experience, and provide valuable business intelligence. Organizations considering implementation often have questions about deployment, which should be addressed early in the planning process.  Defining Reverse ATM Technology
Defining Reverse ATM Technology Advanced Bill Validation Technology
Advanced Bill Validation Technology Integration with Venue Operations
Integration with Venue Operations Understanding the Modern Payment Ecosystem
Understanding the Modern Payment Ecosystem The operational improvements are immediate and measurable. By automating cash acceptance, venues reduce labor costs, shrink theft risk, and eliminate time spent reconciling tills and transporting deposits.
The operational improvements are immediate and measurable. By automating cash acceptance, venues reduce labor costs, shrink theft risk, and eliminate time spent reconciling tills and transporting deposits.  Cash-to-card technology is proving valuable across industries and
Cash-to-card technology is proving valuable across industries and  Core Architecture
Core Architecture Security and Fraud Prevention
Security and Fraud Prevention How to use Reverse ATMs for Marketing and Customer Engagement
How to use Reverse ATMs for Marketing and Customer Engagement Several converging factors have accelerated the demand for self-service solutions across industries.
Several converging factors have accelerated the demand for self-service solutions across industries. Organizations implementing self-service solutions report significant advantages beyond improved customer satisfaction.
Organizations implementing self-service solutions report significant advantages beyond improved customer satisfaction. Artificial Intelligence Integration: AI-powered kiosks can provide more personalized recommendations, understand natural language queries, and learn from customer interactions to improve over time. This makes self-service options more helpful and engaging.
Artificial Intelligence Integration: AI-powered kiosks can provide more personalized recommendations, understand natural language queries, and learn from customer interactions to improve over time. This makes self-service options more helpful and engaging.








